Kardiovaskuläre Forschung
Team:
Dr. H. Bömmel heike.boemmel@uni-wuerzburg.de
Dr. S. Hübner stefan.huebner@uni-wuerzburg.de
Prof. Dr. F. Kleefeldt florian.kleefeldt@uni-wuerzburg.de
Dr. U. Rückschloß uwe.rueckschloss@uni-wuerzburg.de
Dr. N. Wagner nicole.wagner@uni-wuerzburg.de
Dr. B. Upcin berin.upcin@uni-wuerzburg.de
Prof. S. Ergün sueleyman.erguen@uni-wuerzburg.de
Kardiovaskuläre Erkrankungen, wie die Atherosklerose, stehen in der Statistik der zum Tode führenden Krankheiten an erster Stelle. Der Spruch „man wird so alt wie die eigenen Gefäße“ ist nach wie vor aktuell. Ziel unserer Untersuchungen ist es, anhand verschiedener in vitro (endotheliale Migration, Proliferation und Tubebildung), ex vivo (Gefäßring-Assays) und in vivo Modelle (Atherosklerose-Modelle) herauszufinden, wie die endotheliale Barriere geschützt, die Neointimabildung blockiert und die strukturelle Erneuerung geschädigter Blutgefäße therapeutisch gesteuert werden kann.
Im Einzelnen verfolgen wir folgende Ziele:
- Welche Rolle spielen die Gefäßwand-residenten endothelialen und glattmuskulären Vorläufer- oder Stammzellen bei der Entstehung der Neointima und der Atherosklerose?
- Wird die Vaskularisierung atherosklerotischer Plaques durch die Gefäßwand-residenten Stammzellen direkt oder indirekt beeinflusst?
- Da CEACAM1 (Cc1)-KO-Mäuse spontan kleine atherosklerotische Läsionen entwickeln, versuchen wir die dahinter steckenden Mechanismen aufzuklären: im Mittelpunkt stehen hierbei vor allem die durch Cc1 modulierten endothelialen Signalwege, die Bedeutung von Cc1 bei der endothelialen Dysfunktion und eNOS-Aktivität und den oxidativen Prozessen durch NADPH-Oxidase-Aktivität sowie der Wirkung von Isoprostanen und dem Thromboxan-Rezeptor bei der endothelialen Barriere und der Leukozyten-Endothel-Interkation.
- Des Weiteren wollen wir untersuchen, welche Rolle endotheliale und nicht-endotheliale Mikrovesikel mit und ohne Cc1-Expression bei den zuvor genannten Prozessen spielen?
- Wie werden die neuen Blutgefäße stabilisiert und welche Rolle spielen die Gefäßwand-residenten Stammzellen bei diesem Prozess?
- Da Isoprostane die VEGF-induzierte Angiogenese hemmen, versuchen wir in einem vom IZKF geförderten Projekt den Einfluss der Isoprostane auf die regenerative Gefäßneubildung bei myokardialer Ischämie und nach einem Myokardinfarkt, zum einen auf die konventionelle Angiogenese und zum anderen auf die Gefäßwand-residenten Vorläufer- und Stammzellen in der Adventitia der Koronargefäße zu klären.
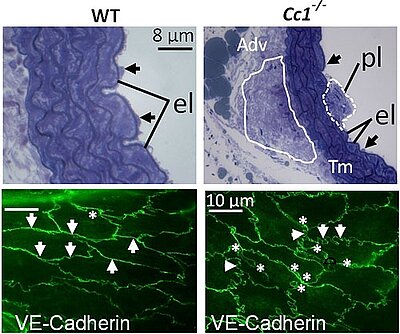
Abb. 1: CEACAM1 (Cc1)-Defizienz und Atherosklerose
Oben: Cc1-/--Mäuse entwickeln kleine atherosklerotische Läsionen (oben) - pl: Plaque (markiert durch eine gestrichelte Linie), el: Membrana elastica, Tm: Tunica media, Adv: Tunica adventitia mit der adventitiellen Reaktion (markiert durch eine Linie), Pfeile: Endothel. Unten: Whole-mount-Immunfärbung der Aorta für VE-Cadherin zeigt deutlich verändertes Endothel mit inter-endothelialen Lücken (*), die auf eine Schädigung der endothelialen Barriere bei Cc1-Defizienz zurückzuführen ist (Najjar et al., AJP Endocrinol Metabol, 2013).
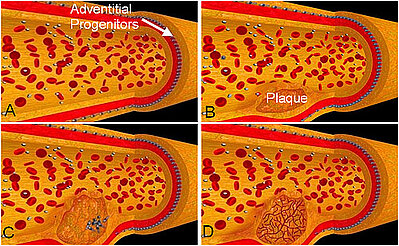
Abb. 2: Progenitorzellen der vaskulären Adventitia und Plaque-Vaskularisierung (A-D):
Entwicklung atherosklerotischer Plaques (B) geht mit einer Mobilisierung der Gefäßwand-residenten Vorläufer und/oder Stammzellen aus der Adventitia (C) einher, die dann zur Vaskularisierung des Plaques beitragen (D) (Tilki et al., Trends in Mol Med, 2011).
Ausgewählte Publikationen:
1. Najjar SM, Ledford KJ, Abdallah SL, Paus A, Russo L, Kaw MK, Ramakrishnan SK, Muturi HT, Raphael CK, Lester SG, Heinrich G, Pierre SV, Benndorf R, Kleff V, Jaffa AA, Lévy E, Vazquez G, Goldberg IJ, Beauchemin N, Scalia R, Ergün S.
Ceacam1 deletion causes vascular alterations in large vessels
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Aug;305(4):E519-29. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00266.2013. Epub 2013 Jun 25.
2. Biermann D, Heilmann A, Didié M, Schlossarek S, Wahab A, Grimm M, Römer M, Reichenspurner H, Sultan KR, Steenpass A, Ergün S, Donzelli S, Carrier L, Ehmke H, Zimmermann WH, Hein L, Böger RH, Benndorf RA.
Impact of AT2 receptor deficiency on postnatal cardiovascular development
PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47916. doi: 1371/journal.pone.0047916. Epub 2012 Oct 29.
3. Banaz-Yaşar F, Gedik N, Karahan S, Diaz-Carballo D, Bongartz BM, Ergün S.
LINE-1 retrotransposition events regulate gene expression after X-ray irradiation
DNA Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;31(9):1458-67. doi: 10.1089/dna.2012.1676. Epub 2012 Jul 30.
4. Blois SM, Tirado-González I, Wu J, Barrientos G, Johnson B, Warren J, Freitag N, Klapp BF, Irmak S, Ergün S, Dveskler GS.
Early expression of pregnancy-specific glycoprotein 22 (PSG22) by trophoblast cells modulates angiogenesis in mice
Biol Reprod. 2012 Jun 28;86(6):191. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.098251. Print 2012 Jun.
5. Klein D, Weisshardt P, Kleff V, Jastrow H, Jakob HG, Ergün S.
Vascular wall-resident CD44+ multipotent stem cells give rise to pericytes and smooth muscle cells and contribute to new vessel maturation
PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020540. Epub 2011 May 26.
6. Nagy N, Freudenberger T, Melchior-Becker A, Röck K, Ter Braak M, Jastrow H, Kinzig M, Lucke S, Suvorava T, Kojda G, Weber AA, Sörgel F, Levkau B, Ergün S, Fischer JW.
Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis accelerates murine atherosclerosis: novel insights into the role of hyaluronan synthesis
Circulation. 2010 Nov 30;122(22):2313-22. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.972653. Epub 2010 Nov 15.
7. Nouvion AL, Oubaha M, Leblanc S, Davis EC, Jastrow H, Kammerer R, Breton V, Turbide C, Ergün S, Gratton JP, Beauchemin N.
CEACAM1: a key regulator of vascular permeability
J Cell Sci. 2010 Dec 15;123(Pt 24):4221-30. doi: 10.1242/jcs.073635. Epub 2010 Nov 16.
8. Ergün S, Tilki D, Klein D.
Vascular wall as a reservoir for different types of stem and progenitor cells
Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Aug 15;15(4):981-95. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3507. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Review.
9. Ha CT, Wu JA, Irmak S, Lisboa FA, Dizon AM, Warren JW, Ergün S, Dveksler GS.
Human pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 1 (PSG1) has a potential role in placental vascular morphogenesis
Biol Reprod. 2010 Jul;83(1):27-35. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.109.082412. Epub 2010 Mar 24.
10. Klein D, Hohn HP, Kleff V, Tilki D, Ergün S.
Vascular wall-resident stem cells
Histol Histopathol. 2010 May;25(5):681-9. Review.
11. Helfrich I, Scheffrahn I, Bartling S, Weis J, von Felbert V, Middleton M, Kato M, Ergün S, Augustin HG, Schadendorf D.
Resistance to antiangiogenic therapy is directed by vascular phenotype, vessel stabilization, and maturation in malignant melanoma
J Exp Med. 2010 Mar 15;207(3):491-503. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091846. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Erratum in: J Exp Med. 2013
12. Tilki D, Hohn HP, Ergün B, Rafii S, Ergün S.
Emerging biology of vascular wall progenitor cells in health and disease.
Trends Mol Med. 2009 Nov;15(11):501-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2009.09.004. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Review.
13. Irmak S, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Singer BB, Ergün S, Tilki D.
Pro-angiogenic properties of orosomucoid (ORM).
Exp Cell Res. 2009 Nov 1;315(18):3201-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.07.024. Epub 2009 Aug 3.
14. Sager HB, Ergün S, Hartmann A, Hoffmann U, Krämer BK, Mihatsch MJ, Weil J.
Expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 in acute rejection of human renal allografts
Transplant Proc. 2009 Jun;41(5):1536-40.
15. Benndorf RA, Schwedhelm E, Gnann A, Taheri R, Kom G, Didié M, Steenpass A, Ergün S, Böger RH.
Isoprostanes inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell migration, tube formation, and cardiac vessel sprouting in vitro, as well as angiogenesis in vivo via activation of the thromboxane A(2) receptor: a potential link between oxidative stress and impaired angiogenesis
Circ Res. 2008 Oct 24;103(9):1037-46.
16. Ergün S, Hohn HP, Kilic N, Singer BB, Tilki D.
Endothelial and hematopoietic progenitor cells (EPCs and HPCs): hand in hand fate determining partners for cancer cells
Stem Cell Rev. 2008 Sep;4(3):169-77. doi: 10.1007/s12015-008-9028-y. Epub 2008 Jul 8. Review.
17. Ergün S, Tilki D, Hohn HP, Gehling U, Kilic N.
Potential implications of vascular wall resident endothelial progenitor cells.
Thromb Haemost. 2007 Nov;98(5):930-9. Review.
18. Kilic N, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Neshat-Vahid S, Irmak S, Obst-Pernberg K, Wurmbach JH, Loges S, Kilic E, Weil J, Lauke H, Tilki D, Singer BB, Ergün S.
Lymphatic reprogramming of microvascular endothelial cells by CEA-related cell adhesion molecule-1 via interaction with VEGFR-3 and Prox1
Blood. 2007 Dec 15;110(13):4223-33. Epub 2007 Aug 30.
19. Chalajour F, Treede H, Gehling UM, Ebrahimnejad A, Boehm DH, Riemer RK, Ergün S, Reichenspurner H.
Identification and characterization of cells with high angiogenic potential and transitional phenotype in calcific aortic valve
Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jul 1;313(11):2326-35. Epub 2007 Mar 14.
20. Zengin E, Chalajour F, Gehling UM, Ito WD, Treede H, Lauke H, Weil J, Reichenspurner H, Kilic N, Ergün S.
Vascular wall resident progenitor cells: a source for postnatal vasculogenesis.
Development. 2006 Apr;133(8):1543-51. Epub 2006 Mar 8.
21. Mühlhausen C, Ott N, Chalajour F, Tilki D, Freudenberg F, Shahhossini M, Thiem J, Ullrich K, Braulke T, Ergün S.
Endothelial effects of 3-hydroxyglutaric acid: implications for glutaric aciduria type I
Pediatr Res. 2006 Feb59(2):196-202.
22. Hansen-Algenstaedt N, Algenstaedt P, Schaefer C, Hamann A, Wolfram L, Cingöz G, Kilic N, Schwarzloh B, Schroeder M, Joscheck C, Wiesner L, Rüther W, Ergün S.
Neural driven angiogenesis by overexpression of nerve growth factor.
Histochem Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;125(6):637-49. Epub 2005 Nov 29.
23. Kilic N, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Wurmbach JH, Loges S, Chalajour F, Neshat-Vahid S, Weil J, Fernando M, Ergün S.
Pro-angiogenic signaling by the endothelial presence of CEACAM1.
J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 21;280(3):2361-9. Epub 2004 Nov 9. Erratum in: J Biol Chem. 2005, 280(12):12064. Vahid, Samira Neshat [corrected to Neshat-Vahid, Samira].
24. Chalajour F, Treede H, Ebrahimnejad A, Lauke H, Reichenspurner H, Ergün S.
Angiogenic activation of valvular endothelial cells in aortic valve stenosis.
Exp Cell Res. 2004 Aug 15;298(2):455-64.
25. Ergün S, Buschmann C, Heukeshoven J, Dammann K, Schnieders F, Lauke H, Chalajour F, Kilic N, Strätling WH, Schumann GG.
Cell type-specific expression of LINE-1 open reading frames 1 and 2 in fetal and adult human tissues
J Biol Chem. 2004 Jun 25;279(26):27753-63.
26. Benndorf R, Böger RH, Ergün S, Steenpass A, Wieland T.
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced migration and in vitro tube formation of human endothelial cells
Circ Res. 2003 Sep 5;93(5):438-47. Epub 2003 Jul 24.
27. Ergün S, Kilic N, Wurmbach JH, Ebrahimnejad A, Fernando M, Sevinc S, Kilic E, Chalajour F, Fiedler W, Lauke H, Lamszus K, Hammerer P, Weil J, Herbst H, Folkman J.
Endostatin inhibits angiogenesis by stabilization of newly formed endothelial tubes.
Angiogenesis. 2001;4(3):193-206.
28. Dührsen U, Martinez T, Vohwinkel G, Ergün S, Sun L, McMahon G, Dürig J, Hossfeld DK, Fiedler W.
Effects of vascular endothelial and platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibitors on long-term cultures from normal human bone marrow
Growth Factors. 2001;19:1-17.
29. Wagener C, Ergün S.
Angiogenic properties of the carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1.
Exp Cell Res. 2000 Nov 25;261(1):19-24. Review.
30. Ergün S, Kilic N, Ziegeler G, Hansen A, Nollau P, Götze J, Wurmbach JH, Horst A, Weil J, Fernando M, Wagener C.
CEA-related cell adhesion molecule 1: a potent angiogenic factor and a major effector of vascular endothelial growth factor
Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):311-20.
31. Fink C, Ergün S, Kralisch D, Remmers U, Weil J, Eschenhagen T.
Chronic stretch of engineered heart tissue induces hypertrophy and functional improvement.
FASEB J. 2000 Apr;14(5):669-79.
32. Lamszus K, Schmidt NO, Ergün S, Westphal M.
Isolation and culture of human neuromicrovascular endothelial cells for the study of angiogenesis in vitro
J Neurosci Res. 1999 Feb 1;55(3):370-81.
33. Ergün S, Harneit S, Paust HJ, Mukhopadhyay AK, Holstein AF.
Endothelin and endothelin receptors A and B in the human testis.
Anat Embryol (Berl). 1999 Mar;199(3):207-14.
34. Ungefroren H, Ivell R, Ergün S.
Region-specific expression of the androgen receptor in the human epididymis.
Mol Hum Reprod. 1997 Nov;3(11):933-40.
35. Ergün S, Kiliç N, Fiedler W, Mukhopadhyay AK.
Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in normal human testicular tissue.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997 Jul 4;131(1):9-20.